OpenBao: Securing the Future of Open Source Secrets Management
published at 07-28-2025 by Max Körbächer
In today's complex technology landscape, managing secrets such as API keys, passwords, certificates, and other sensitive data has become one of the biggest challenges for businesses. That's why Liquid Reply supports OpenBao, an open-source system for managing secrets and encryption based on identity, to secure data management in the cloud era.
What is OpenBao?
OpenBao is an identity-based system for managing secrets and encryption. A secret is anything you want to strictly control access to, such as API encryption keys, passwords, and certificates. OpenBao provides encryption services protected by authentication and authorization methods.
Originally spun off from HashiCorp Vault, OpenBao has evolved into a community-driven project that meets the growing need for secure, scalable, and transparent secrets management in open-source environments. The platform enables organizations to centrally manage all their credentials, reducing the security risks associated with spreading credentials across multiple systems and applications.
The OpenBao approach: authentication, authorization, and access
OpenBao works on a simple but powerful principle: OpenBao validates and authorizes clients (users, machines, apps) before granting them access to secrets or stored sensitive data.
The system operates on a four-step workflow:
- Authentication: Clients provide information to verify their identity using trusted authentication methods.
- Validation: OpenBao validates clients using third-party sources such as GitHub, LDAP, or AppRole.
- Authorization: Clients are checked against security policies that determine which resources they are allowed to access.
- Access: After successful authentication and authorization, OpenBao issues tokens that enable access to specific secrets and functions.
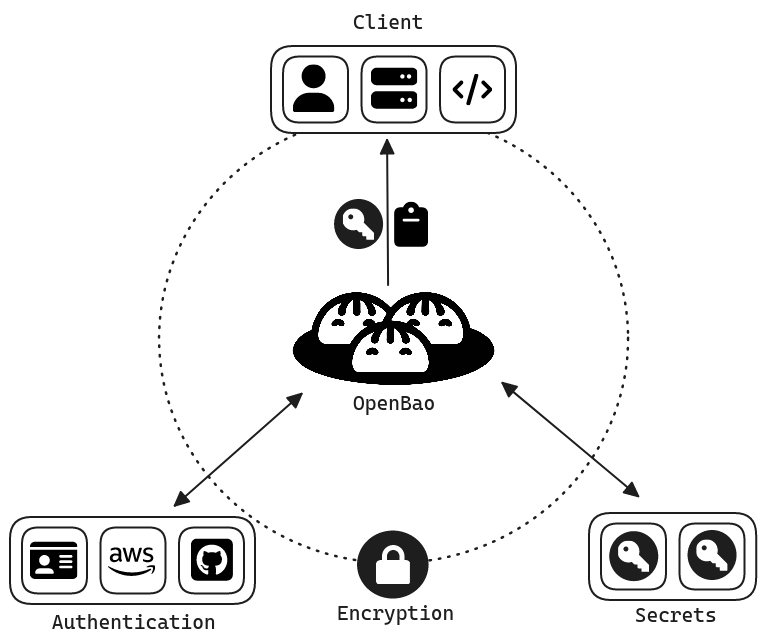
Source: https://openbao.org/docs/what-is-openbao/
Key features of OpenBao
Secure storage of secret data
Any key/value secrets can be stored in OpenBao. OpenBao encrypts these secrets before writing them to persistent storage, so access to raw storage is not sufficient to access your secrets.
Dynamic secrets
Instead of storing static credentials, OpenBao can generate secrets for systems such as Kubernetes or SQL databases as needed. These dynamic secrets are automatically revoked when they expire, significantly reducing the risk of exposure.
Data encryption
OpenBao offers encryption as a service with centralized key management, simplifying both encryption of data in transit and at rest. Because encryption within the OpenBao environment is managed by the OpenBao security team, developers can focus exclusively on application logic.
Comprehensive audit trail
Every action in OpenBao is logged, providing detailed audit trails that are essential for regulatory compliance and incident response.
Leasing and renewal system
All secrets created in OpenBao are associated with a lease. When a lease expires, the system automatically revokes the secret, providing protection against potential security breaches and unauthorized access.
Secret trail and revocation
OpenBao has built-in support for revoking secrets and supports not only the revocation of individual secrets, but also a tree structure of secrets, e.g., all secrets read by a specific user or all secrets of a specific type, enabling a quick response to potential incidents.
An important milestone: joining the OpenSSF
In a significant development for the project, OpenBao has joined the Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) as a newly accepted sandbox project. This step represents a strategic alignment with the broader open source security community.
“Joining the OpenSSF is a dream come true,” said Alex Scheel, chair of the OpenBao Technical Steering Committee.
The transition from LF Edge to OpenSSF reflects the project's evolution and its commitment to meeting the needs of security professionals and open source maintainers.
This new partnership enables OpenBao to collaborate with various OpenSSF working groups and interest groups, particularly to strengthen best practices for secret management in open source projects.
Latest version – Namespaces: Enabling true multi-tenancy
One of OpenBao's newest features is the recently announced Namespaces feature. Namespaces in OpenBao are logical partitions within a single OpenBao instance that act as isolated environments where teams, organizations, or applications can operate independently of each other.
Why namespaces are important
Strong isolation between teams, business units, or clients becomes increasingly important as organizations grow, especially when dealing with sensitive data. Namespaces enable:
- Secure multi-tenancy: Each client works in its own isolated namespace with strictly limited permissions.
- Delegated administration: Namespace administrators can manage their own policies, secret engines, and authentication methods.
- Self-service capabilities: Reduces the burden on operators at the cluster level while empowering teams.
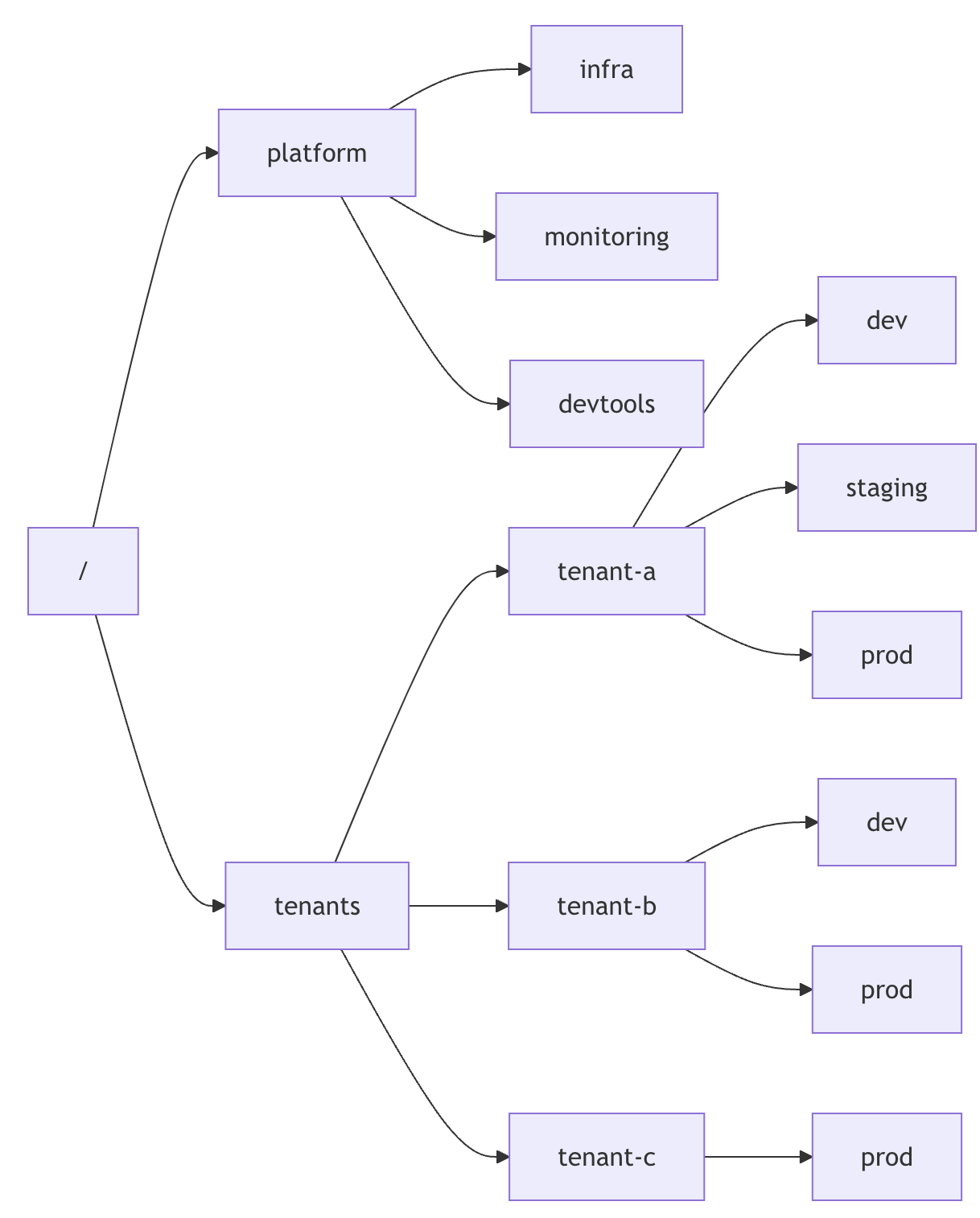
An example namespace structure to separate tenants and the platform team.
Outlook
The path to horizontal scalability
Namespaces are the first step on OpenBao's path to horizontal scalability. The vision includes support for lazy loading of namespaces and mounts so that clusters can efficiently serve workloads with many rarely used resources.
The path to secure, self-managed multi-tenancy
The sealing mechanism per namespace provides a more robust and flexible multi-tenancy solution that gives tenants more control over their data security and availability within the OpenBao ecosystem.
Declarative self-initialization and profiles
Declarative self-initialization is a new feature that enables automatic configuration on first startup through a flexible profile system. This advancement eliminates the need for manual initialization steps and enables fully automated deployments in modern infrastructure-as-code environments.
The profile system
At the heart of this feature is a new profile system that provides a framework for cross-platform communication and request orchestration. The profile system processes configuration blocks into structured API requests and supports dynamic data sources and request chaining for complex initialization workflows. The system implements the request/response pattern, supports chained operations, and accepts request handlers and parsed profile configurations. In this workflow, the input can be one of the following types: value, environment variable, file, request, or response.
Key components:
- Configuration parser: Processes HCL configuration blocks into executable requests
- Source code generators: Process dynamic data from environment variables, files, and previous responses
- Request handler: Executes template-based requests to internal APIs
- History manager: Enables data flow between sequential operations and keeps logs.
Liquid Reply's contribution to OpenBao
As a leading expert in cloud-native transformations, Liquid Reply is making a significant contribution to the OpenBao project, particularly in the development of the namespaces feature.
This contribution is in line with Liquid Reply's expertise in platform engineering and cloud-native development. As specialists in multi- and hybrid cloud solutions, we understand the critical importance of robust secret management in complex distributed systems. Our commitment to OpenBao reflects our desire to promote open-source security tools that enable companies to securely implement cloud-native transformations.
Our commitment to open-source security
Liquid Reply's contribution to OpenBao is part of our comprehensive commitment to the open-source community. As a company that helps organizations navigate complex cloud-native transformations, we understand the critical role that secure and scalable secret management plays in modern infrastructures.
Our expertise in Kubernetes, site reliability engineering, and operational enablement positions us well to contribute to projects like OpenBao, which lay the foundation for secure cloud-native operations.
Europe's promise
The development of OpenBao is partly funded by the IPCEI-CIS (Important Project of Common European Interest – Next Generation Cloud Infrastructures and Services) in collaboration with SAP and is an important addition to the ApeiroRAopen source projects, which aim to build a powerful cloud edge infrastructure based on European values. The ApeiroRA open source projects are managed independently by the NeoNephos Foundation.
Get involved
OpenBao represents the future of open source secret management—secure, scalable, and community-driven. Whether you are a security professional, developer, or organization looking to improve your secret management, OpenBao offers a robust, transparent alternative to proprietary solutions.
Ready to explore OpenBao?
- Visit the OpenBao GitHub repository
- Join the discussion on OpenSSF Slack
- Connect with the community on Matrix
As OpenBao continues its journey within the OpenSSF, organizations worldwide can benefit from a secret management solution that prioritizes security, transparency, and community collaboration. The future of secret management lies in open source, and OpenBao is leading the way.